Earlier in the week I wrote about the basics of good email communication, the three Ts. In this follow-up I want to cover a few more complex things which didn't fit in the previous post, particularly around the theme of an email newsletter.
Why do people unsubscribe from mailing lists and newsletters?
Reasons people no longer want to receive a regular email from an organisation include, in ascending order of importance according to Litmus: Found an alternative way to get the same info, Preferred to seek out info on their own, Found the content irrelevant, Received too many emails generally, Found the content to be repetitive or boring over time.
And in First Place? 54% of people said the reason they unsubscribed was this: Emails came too frequently. Don't over-saturate your audience - pick your moments, based on THEIR needs, the lifecycle of their work, and on how much vital information you have to impart. Which leads us to...
So how frequently should I email?
In Part 1 of this post I talked about the importance of being Timely - emailing at the right time of the day so that your email is received both at a time when people actually read emails and when yours isn't buried under a pile of other emails coming in at the same time. 3pm appears to be the sweet spot.
There's another aspect to being timely though. Firstly, Monday appears to be the best day on which to send an email newsletter - for all the reasons you'd imagine (people are still full of vim and vigour early on in the week, and not yet weighed down by all the things they wished they'd got done but ran out of time to do).
Secondly, I believe it's really important NOT to email to a fixed schedule, for example the first Monday of every month. A vital aspect of good communication is not wasting opportunities by communicating when you don't need to - it reduces the value of your communication overall and edges you closer to becoming part of the white noise. So send your newsletter or other 'important updates' email only when there's a weight of useful things to say, rather than just when it's the time you usually send it. Communicate because your audience NEEDS to hear what you have to say, rather than because you need to send a monthly update.
How long should my subject line be?
I mentioned in Part 1 that I think the Subject Line is hugely important, and that calling your email 'Newsletter' is a recipe for being completely ignored. You need a decent title, one which gives people a specific reason to open the email; a benefit to them.
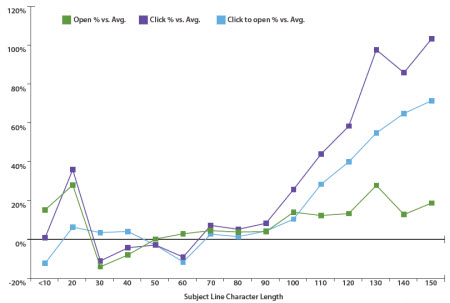
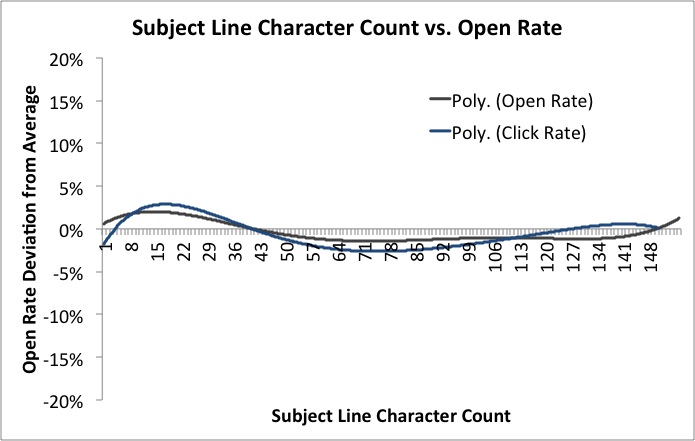
As to how long this subject line should be, there is conflicting evidence about this. EmailAudience found that very short worked well, medium length worked REALLY badly, and very long (tweet length subject lines, basically) worked fantastically.
However MailChimp analysed 12 billion emails and concluded 'Subject line length means absolutely nothing'! If you compare the graphs showing the two companies' findings, they do actually follow broadly the same pattern - short and long are good, medium length doesn't do much for anyone. It's just that how much of a difference this makes is clearly reflected as being much smaller by MailChimp.
They conclude with this very sensible statement which makes a good point about Subject Line length and the kinds of devices and platforms your audience are reading on.
“Your audience is chock-full of individuals with different reading habits, interests, and demographics. Maybe my audience is full of Apple fanboys and every one of them reads my newsletter on their iPhone. Well, then the subject line they see might need to be shorter for their small screen. Or maybe my newsletter is geared toward businessfolk who mostly run Outlook. In that case, maybe a longer subject is more acceptable.”
Like so many things, it comes down to understanding your audience. Which takes us neatly on to...
How can I measure and track the impact of my email?
There are elaborate things you can do with Gmail to track open-rates of emails, but I think that's much more important in traditional business than it is in non-profit comms. More important is to measure and track the impact - essentially, do people ACT on the email, and can I influence how often this happens by changing when I send the email, the subject line, the tone, the length and so on?
If your email is a just general update, measuring impact is very hard to do. If, however, it includes a Call to Action, and that action has a website involved - e.g. 'Try our new online resource [link to resource]' or 'Come to our workshop [link to booking form]', it becomes possible to see how effective the email is by measuring the Engagement Rate. This is the number of clicks on the link divided by the number people who received the email - so take a really basic example, if you email 100 people and 30 click the link, the Engagement rate is 30%.
How do you find out how many people click on the link? You use a unique URL created especially for the email via bit.ly. Bit.ly is a URL shortening service (useful in itself) which provides two fantastic functions for Comms purposes - it allows you to customise the URL, and it counts the number of times that specific customised URL is used.
(So for example, at the end of the 10 Tiny Tips for Trainers slidedeck from a couple of weeks back, I put in a customised bit.ly URL for people who found the presentation on Slideshare, and wanted to read the blogpost which accompanied it on here - a lot more people see my slides than see this blog. The reason I used bit.ly was just to make a short, memorable URL - I chose bit.ly/10TinyTips which is a lot easier to fit on a slide in large letters than http://www.ned-potter.com/blog/2014/8/8/10-tiny-tips-for-trainers! - but it also gives me the stats. So I know that 225 people clicked on the link in the slides, because that link didn't appear anywhere else.)
So going back to the email newsletter - if you're launching a resource or promoting an event, and you want to know how effective your email has been, use a customised bit.ly URL to see how many people clicked your link. If half the people you email click on the link you've included, that's a pretty fantastic rate of return as these things go. Build on whatever formula you used and do it again! If only 5% click, then do things differently next time - perhaps change the subject line, or make the call to action more prominent, or email at a different time of the day or week.
Incidentally, another possibility bit.ly allows is to compare effectiveness of promotional activities. So you have one bit.ly URL for your new resource that you use in emails, one that you use on Facebook, and another you use on Twitter. Then you compare the stats for each, with the overall stats for the resource, and see which communication method is the best way to get people to use your stuff...
Should I care about email preview panes?
If your audience are young (University students, for example) then yes, this matters a little bit. According to ConvinceandConvert, 84% of 18-34 year olds use an email preview pane. I am 34 and I do this! I have a preview pane in both Outlook and Gmail for work, where I can - but not in Yahoo for my personal email, where I've never worked out how. I much prefer a preview.
This means these users will see the first few lines of the email (depending on how big they've set their pane) BEFORE they click to open. Worst-case scenario is they dislike what they see so much they never get as far as opening the email. The best-case scenario is they are enticed or inspired by the preview, and when they open the email they are fully engaged with its contents. So, as with so many media in the web 2.0 age, the important thing here is to hit the ground running. No long intros, no scene setting - just useful, headline information right at the top. It's using the journalism model, rather than the academic paper model - put your conclusions at the start.
Are there any useful email tools I should know about?
I think MailChimp looks great for non-profits. You'd probably need to use the paid-for version, but if email is an important part of your marketing strategy, and you can afford it, then MailChimp is worth it because of the level of control, and of impact measurement, it gives you.
I'm a big fan of Scribd (as a creator rather than a consumer - don't be put off by its homepage which is aimed at the latter!) - it takes PDFs and turns them into web documents. So if your email newsletter is a PDF, I cannot stress enough how people don't click on and open PDFs nearly as much as we'd hope they do, so put in a link to a Scribd version (or embed it in the email if that's possible with the tools you use). Not only does this make the newsletter more easily accessible, it allows it to be discovered on the web, and it gives you built-in usage statistics for how it much it's being read too.